What is Mechanical circulatory support?
Mechanical Circulatory support denotes the use of devices in patients with heart failure and shock, in order to support blood circulation to vital organs and body tissues to sustain life, when the pump function of the heart has failed despite using intra-venous medications.
What are the types of MCS?
MCS includes those used as an emergency to tide over an acute situation which includes the short term MCS devices, which include the Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP), Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenator (ECMO) and the Impella devices and the ones used in chronic refractory heart failure, which are the Ventricular Assist Devices (VAD).
What is Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)?
IABP is a MCS device which is used to support patients with low BP and cardiogenic shock, usually doing a massive heart-attack when there is a sudden or acute heart or pump failure of the left ventricle.
During shock less blood enters the arteries of the heart and therefore the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough blood or oxygen to function efficiently. The balloon pump is very useful to reduce strain on the heart and helps to improve the blood circulation in the coronary arteries and thus improves blood supply and oxygenation of the heart muscle. This helps the heart muscle to recover during the period of shock and helps the pumping function to recover and improve.
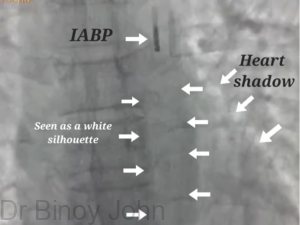
IABP consists of a large balloon which is inserted via the Femoral artery at the groin, under local anaesthesia. The balloon is advanced and positioned in the descending portion of the Aorta. The balloon is connected to an external console which is programmed to alternately inflate and deflate the balloon with Helium, at intervals set by the physician. When it inflates it is seen as a white silhouette against the heart shadow. (See image) The image shows IABP placed in a patient who presented with massive extensive anterior wall heart attack and shock. Angioplasty to LAD artery was performed successfully and he was placed on IABP support for three days and was removed when his blood pressure improved and recovered from the shock. The patient was discharged a week later.
What is Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)?
ECMO is a Mechanical Circulatory Support device which is used for short-term therapy of patients in shock who are deteriorating or unstable, where the heart is not able to effectively pump oxygenated blood to the brain and other vital organs for their proper functioning.
The VA (Veno-Arterial) -ECMO is a rapid mode MCS which is used as a last resort salvage therapy in patients with cardiogenic shock. ECMO is essentially a form of Cardio-Pulmonary By-pass where de-oxygenated or impure blood is passed via an inflow venous cannula inserted commonly in the femoral vein at the groin and passes into an external Membrane-Oxygenator machine, where the blood is oxygenated and returned to the body through another out-flow arterial cannula placed commonly in the femoral artery at the groin.
Survival rates to discharge in refractory cardiogenic shock, with the use of ECMO depends on the clinical indication and varies from 39 to 80%. Bleeding is one of the issues especially at the femoral cannulation site.
Survivors are usually candidates for a subsequent Ventricular Assist Device and rarely Heart Transplantation.
What is Impella Device?
The normal pumping efficiency of the heart at 55-70%, helps in supplying blood to the entire body with a Cardiac Out-put of upto 6 litres per minute. However this pumping efficiency can come down to very low levels such that the heart is not able to pump enough blood, oxygen and nutrition to the heart itself and the various organs and tissues of the body and thus cannot sustain life, a condition called Cardiogenic Shock. This situation is especially common during massive heart attacks. In such situations, when intra venous medications are not effective, mechanical devices like the Impella device can be used to maintain a good cardiac out-put, while the pumping recovers. This Impella device is especially useful in a situation of a massive heart attack, while an emergency life-saving angioplasty (Read section: Primary angioplasty) is being performed for the block causing the heart-attack.
The Impella device is a catheter which has an end shaped like a pig’s tail and can be inserted into the left ventricular chamber of the heart with poor pumping function. There is a motor which helps in sucking out blood from the left ventricle and supplies blood to various parts of the body. The Impella device comes in different models depending on its pumping efficiency or the blood out-put generated.
The Impella can be used only for a short period of up to 7 days although it has been used off-label, for up to 27 days in some pioneering centres.
How is the Impella device placed?
The Impella device doesn’t need the chest or heart to be opened but can be placed by pin hole techniques (a.k.a: Percutaneous techniques), just like an angioplasty is performed, via the Femoral artery in the leg region or via the Axillary artery in the region of the collar bone.
Expertise: Dr Binoy John under went advanced heart failure, MCS & Cardiac transplant medicine observership at Cedar Sinai Heart Institute and is involved in the active management of Advanced Heart Failure patients






