What is a Coronary Angiogram?
Video with Live narration by Dr Binoy John – English
What are coronary arteries?
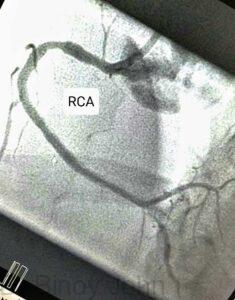
The heart is a mechanical pump. The function of the heart is to pump blood and thus supply energy to the different parts of the body. The heart pumps on an average of 72 times per minute which makes it 100,000 times per day and 30,00,000 times per month. For the heart to function as an efficient mechanical pump it also needs blood. This blood is supplied to the heart via three arteries called coronary arteries, which run on the surface of the heart. The one on the right which supplies blood to the right and inferior surface of the heart is called the Right coronary artery (RCA). (See image)
The left surface of the heart is supplied by a short left main (LM) artery which then branches into two large coronary arteries called the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the left circumflex (LCx) artery. (See image)
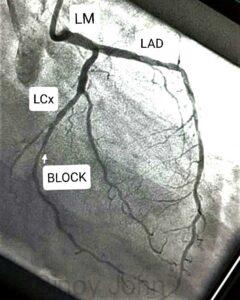
Occasionally there can be a third artery arising from the LM called the ramus intermedius artery. The coronary arteries are on an average 2- 4 mm in diameter and they arise from the aorta, which is the largest and first artery into which the pumped blood from the heart enters.
What is a coronary angiogram?
When blocks occur inside the coronary arteries they can cause a heart attack or symptoms like chest-pain or breathing difficulty on walking or exertion. To know if there are significant blocks inside these arteries there are indirect non-invasive tests like a treadmill test. However, when the treadmill test is positive or when the clinical suspicion of a block is very high, a confirmatory test is required to visualize the blocks, the gold-standard for which is the coronary angiogram.
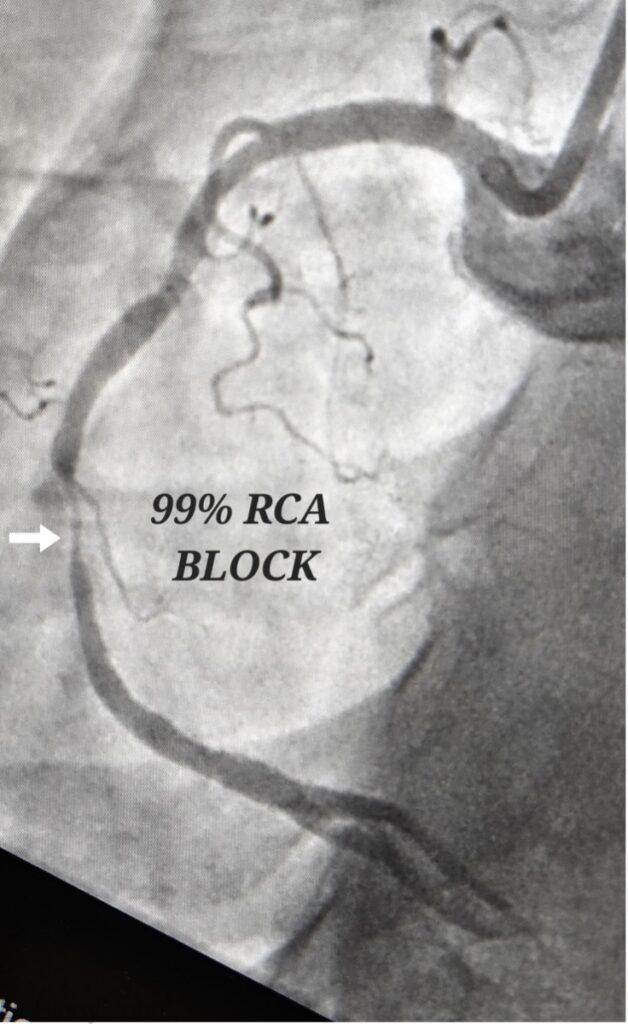
The coronary angiogram is a procedure which uses x-rays to capture dynamic or moving images of the coronary arteries. As blood is not radio-opaque, coronary angiogram requires a radio-opaque dye or contrast to be injected directly into the coronary arteries by means of a catheter. The contrast displaces the blood to obtain a clear image or luminogram of the inside of the arteries. Any blocks that are present will be seen as narrowings in the angiogram images. (See image)
What are the access sites for performing a coronary angiogram?
A coronary angiogram can be done from the leg/groin via the femoral artery, which is a subsidiary branch of the aorta or it can be done from the hand/wrist via the radial artery which is also a subsidiary branch of the aorta. Current guidelines recommend coronary angiograms and angioplasties to be done via the radial artery access except in certain exceptional circumstances.
Expertise: Dr Binoy John performs 99% of his angiograms via the radial artery in the hand and he is one of the earliest interventional cardiologists in South India to perform angiograms and angioplasties via the hand or radial artery access.






